

7.1 INTRODUCTION
7.1.1 The purpose of this section of the Report is to describe the structure of the Landscape GIS used to collate survey information, and provide basic instructions as to its functions and operations. Further detailed information is contained in the separate GIS Manual produced for the Study.
7.2 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING THE LANDSCAPE CHARACTER MAP
LCM GIS Database
7.2.1 The GIS database contains spatial data, attribute tables, photo records taken during the field survey, as well as the Landscape Character Map (LCM).
System Requirements
7.2.2 In order to make use of the GIS database, users need to have the following software packages installed on their workstation platforms (Windows NT/2000/XP).
ESRI ArcGIS 8.2 or higher (ArcView/ArcEditor/ArcInfo);
Apple QuickTime Player 5.0 or higher, which can be downloaded from http://www.apple.com/quicktime/;
Any image viewer software which supports JPG format. e.g. Internet Explorer (IE);
Adobe Acrobat Reader 5.0 or higher.
7.2.3 Users must also have at least 1.5GB empty space on their local computer hard disk drive to incorporate graphic and textual data.
Installation Procedure
7.2.4 In order to make use of the GIS database and to ensure optimum system performance, users are recommended to follow the steps listed below:
Copy the whole LCM_GIS folder from the DVD provided to your local hard disk D:\ drive, keep the original directory structure;
Once copied, your LCM GIS database in D:\ should look like this:
Open the LCM Map Document;
Double click the LCM_GIS.mxd (ArcMap document) in the MXD folder as illustrated below.
7.2.5 This will open the ArcMap application and the Landscape Character Map project will display the map in the layout window as below.
7.3 DATABASE STRUCTURE
Introduction
7.3.1 The relevant spatial information being employed in the Landscape Value Mapping exercise includes layers of spatial data used during the production of the Preliminary Landscape Character Map, completed landscape features, final re-classified LCA polygons and each LCA’s corresponding site field survey photographs. In addition, relevant base map layers are also included in the Landscape GIS database for reference purposes (see Table 7.1). In total, 3 personal geodatabases under the LCM_GIS have been constructed, namely: Landscape Character Area.mdb; Landscape_Class.mdb and Landscape_Features.mdb.
Table 7.1 GIS Database
Folder Name Sub Folder Name Data Description LCM_GIS Landscape Classification Natural & Human Features layers Personal GDB Landscape Evaluation Landscape Features layers Personal GDB Landscape Character Area Final re-classified LCA layer Personal GDB Photos LCA Field survey photos MOV, JPG LCA Description LCA description files Mxd ArcGIS project document ArcMap MXD Landscape Classification
7.3.2 Landscape_Class.mdb has been sub-divided into several feature datasets including both human and natural features, such as: Ecological Habitats, Geomorphology and Topography, Hydrology, Vegetation, Building footprint, Historical Sites, Land Use, Railways and Road Pattern. The detailed data layers are listed in Table 7.2 below.
7.3.3 In addition, a digital elevation model (DEM) is also included in the Landscape Classification folder. The file is in ESRI raster GRID format with a resolution of 50m, covering the whole territory. This dataset is derived from Land Information Centre (LIC) 1:20,000 topographic data.
Table 7.2 Detailed Descriptions of Landscape_Class.mdb
Feature Dataset Feature Class Description Data Source (or basis of Derivation) Geometry Type Building Footprint BUILDING_5K_ANNOCHI Buildings Chinese annotation LIC B5000 datasets ANNO BUILDING_5K_ANNOENG Buildings English annotation LIC B5000 datasets ANNO BUILDING_5K_ANNOHSNO Building House Number LIC B5000 datasets ANNO BUILDING_5K_POLYGON Buildings with types where available. LIC B5000 datasets ANNO Ecological Habitats ECO_COASTTYPE Coastline categorised into various natural types. Derived from AFCD Habitat Map LINE ECO_INTERTIDAL Polygons representing locations of inter-tidal LCTs such as mudflat and mangrove. Derived from AFCD Habitat Map POLYGON Geomorphology and Topography GEO_BEACH Gazetted and non-gazetted beaches. Derived from AFCD’s Habitat Map POLYGON GEO_BEACH_GAZETTED Gazetted beaches Derived from AFCD’s Habitat Map POINT GEO_BOULDER Areas of boulder material from API Derived from GEO boulder API dataset POLYGON GEO_CONTOUR_20K_ANNO Annotation of B20000 contours Derived from LIC 1:20,000 topographic data ANNO GEO_CONTOUR_20K_ARC Contour lines with heights. Derived from LIC 1:20,000 topographic data LINE GEO_GEOLOGY_SOLID Solid geology at various scales Derived from GEO geological dataset POLYGON GEO_GEOLOGY_SUPERFICIAL Superficial geology at various scales Derived from GEO geological dataset POLYGON GEO_RELIEF_1K_ANNO Annotation of B1000 Relief features Derived from LIC 1:1000 topographic data ANNO GEO_RELIEF_1K_ARC Slope tops and bottoms. Derived from LICs 1:1,000 topographic data LINE GEO_SPOTHT_20K_ANNO Annotation of B20000 Spot height features Derived from LIC 1:20,000 topographic data ANNO GEO_SPOTHT_20K_POINT Spot heights. Derived from LICs 1:20000 topographic data POINT Historical Sites HIST_ARCHSITE Archaeologically significant sites. From LCSD. POLYGON HIST_HERITAGESITE Heritage buildings and sites. From LCSD. POINT Hydrological features HYD_COAST Coastline Derived from 1:5,000 topographic data LINE HYD_RIVER_5K_ANNOCHI Chinese Annotation of B5000 hydrology features Derived from 1:5,000 topographic data ANNO HYD_RIVER_5K_ANNOENG English Annotation of B5000 hydrology features Derived from 1:5,000 topographic data ANNO HYD_RIVER_5K_ARC Rivers and streams. Derived from LIC 1:5,000 topographic data used to assist in interpretation. LINE Land Use LU_FISHPOND Gei Wei fish ponds From AFCD’s Habitat Map POLYGON LU_LANDUSE Broad Land-use of Hong Kong PlanD Broad Landuse of Hong Kong dataset POLYGON LU_OZPZONE Outline Zoning Plan PlanD OZPs POLYGON LU_SBVC2001 Street block boundaries From PlanD SBVC2001 data set POLYGON LU_VILLAGE Rural villages Village boundaries from OZP. POLYGON Railways RAILWAY_5K_ANNOCHI Chinese Annotation of B5000 Railway features Derived from LIC 1:5,000 data ANNO RAILWAY_5K_ANNOENG English Annotation of B5000 Railway features Derived from LIC 1:5,000 data ANNO RAILWAY_5K_ARC Railways. for presentation purpose only. LINE Road and Street Patterns ROAD_5K_ANNOCHI Chinese Annotation of B5000 Road features Derived from LIC 1:5,000 data ANNO ROAD_5K_ANNOENG English Annotation of B5000 Road features Derived from LIC 1:5,000 data ANNO ROAD_5K_ARC Roads Derived from LIC 1:1:5,000 data for presentation purpose only. LINE Vegetation Types VEG_GSWB Polygons of Grassland, Shrubland, Woodland and Badlands Derived from PlanD Broad Landuse Map POLYGON Landscape Evaluation
7.3.4 The bilingual language version of the landscape feature data layers is provided in two-separated personal geodatabases: Landscape_Features_Chi.mdb and Landscape_Features_Eng.mdb. These layers indicate significant areas and features of landscape value. Tables 7.3 and 7.4 outline the associated datasets in the Landscape GIS database.
Table 7.3: Map Layers Used for Landscape Evaluation (Chinese Version)
Feature Dataset Feature Class Description Geometry Type Sense of Place PLACE_LINE Streams, Footpaths, Ridgelines, Coastline, Escarpment, Dam, Street, Bridge LINE PLACE_POINT Peak, Waterfalls, Geomorphologic features including Rocks, Arches & Blow Holes, Crags, Cliffs, Building POINT PLACE_POLYGON Beach, Rocky Foreshore, Mud flat, Small Island, Bay-inlet, Reservoirs, Villages, Valley, Badland, Landform, Ridge, Upland Plateau, Country Park, Public Open Space, Marine Basin, Building-extensive POLYGON Visual Attractor POSVAL_LINE Streams, Footpaths, Ridgelines, Coastline, Escarpment, Landmark Structures LINE POSVAL_POINT Peak, Waterfalls, Geomorphologic features including Rocks, Arches & Blow Holes, Crags, Cliffs, Landmark Buildings (localised) POINT POSVAL_POLYGON Beach, Rocky Foreshore, Mud flat, Small Island, Bay-inlet, Reservoirs, Villages, Valley, Badland, Landform, Ridge, Upland Plateau, Country Park, Public Open Space, Marine Basin, Landmark Structures (extensive) POLYGON Others HIST_BUILDING Historic buildings POINT SSSI Site of Special Scientific Interest POLYGON Table 7.4: Map Layers Used for Landscape Evaluation (English Version)
Feature Dataset Feature Class Description Geometry Type Sense of Place PLACE_LINE Streams, Footpaths, Ridgelines, Coastline, Escarpment, Dam, Street, Bridge LINE PLACE_POINT Peak, Waterfalls, Geomorphologic features including Rocks, Arches & Blow Holes, Crags, Cliffs, Building POINT PLACE_POLYGON Beach, Rocky Foreshore, Mud flat, Small Island, Bay-inlet, Reservoirs, Villages, Valley, Badland, Landform, Ridge, Upland Plateau, Country Park, Public Open Space, Marine Basin, Building-extensive POLYGON Visual Attractor POSVAL_LINE Streams, Footpaths, Ridgelines, Coastline, Escarpment, Landmark Structures LINE POSVAL_POINT Peak, Waterfalls, Geomorphologic features including Rocks, Arches & Blow Holes, Crags, Cliffs, Landmark Buildings (localised) POINT POSVAL_POLYGON Beach, Rocky Foreshore, Mud flat, Small Island, Bay-inlet, Reservoirs, Villages, Valley, Badland, Landform, Ridge, Upland Plateau, Country Park, Public Open Space, Marine Basin, Landmark Structures (extensive) POLYGON Others HIST_BUILDING Historic buildings POINT SSSI Site of Special Scientific Interest POLYGON Landscape Character Area
7.3.5 A geodatabase named Landscape Character Area.mdb contains a single GIS data layer with 943 LCA polygons. Each of them represents a particular LCA and is coded with a numeric identifier corresponding to its LCT. The attributes with the feature polygons provide clear identical information for each LCA (see Table 7.5).
Table 7.5: Attribute Information Associated with Polygons
Item Name Description Data Type Length OBJECTID_1 I nternal unique object identifier code for polygon in file Integer - Shape Internal geometry linkage Geometry - RD_LCA Unique identifier for each Landscape Character Area (LCA) polygon Text 50 RD_LCA_NAM Full name of each LCA Text 254 RD_LCT Classified Landscape Character Type code for LCA polygon Text 50 LCT Full name of each Landscape Character Type (LCT) V_O_LCA Overall Landscape Value for each LCA Text 128 V_SP_CONDT Overall Landscape Condition for each LCA Text 128 V_VT Significant Change Ongoing Value Text 12 SHAPE_LENGTH Internal perimeter for each LCA polygon Double - SHAPE_AREA Internal area for each LCA polygon Double - Layer Display On and OFF
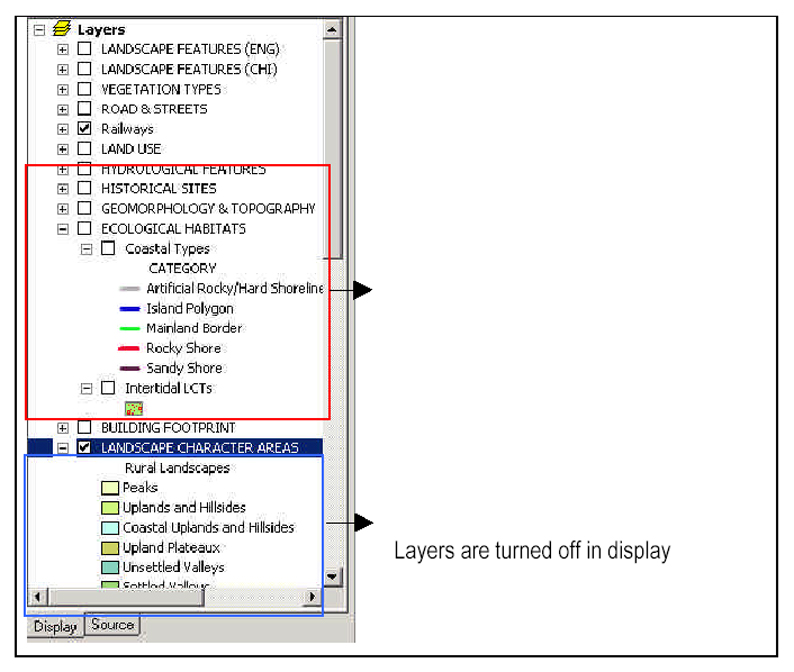
7.3.6 As long as the layers are already in the ‘Layers’ Table of Contents, you are allowed to turn on and off the layers on display, to enhance the visualization. To display the layers, turn on the layers by checking the boxes in the ‘Layers’ Table of Contents.
7.4 BASIC MAP DISPLAY CONTROLS
Introduction
7.4.1 Users are allowed to view the data in different ways by employing the ‘Tools’ toolbar with its various button. Details are as shown below:
Identify and Query
7.4.2 Selection of features can be achieved by building an expression in the ‘Select By Attributes’ tool, under Location in the menu bar. Structured Query Language (SQL) is a powerful language available to define one or more criteria. These may consist of attributes, operators and calculations. Users have to input the relevant layer and the corresponding criteria. Those features which meet the criteria defined in an SQL, would then be selected. For example, a search criterion: “LCT “ = ‘Residential Urban Landscape’ would reveal features shown below.
Create and Manage Spatial Bookmarks
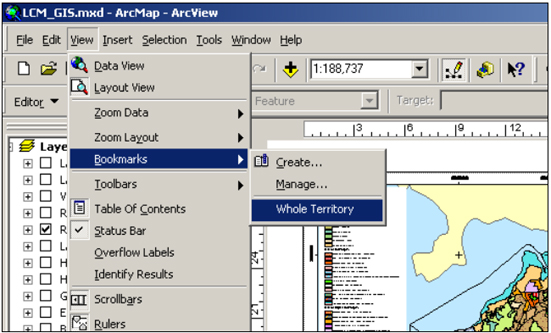
7.4.3 Users can identify a particular geographic location at a particular map scale, and refer to the same extent later by creating a Spatial Bookmark. This provides an easy way to retrieve a predefined map extent by accessing the bookmark. To take advantage of Spatial Bookmarks, three basic steps are involved:
To Create a bookmark - users can create bookmarks from a Find Dialog Box or the Identify Results Dialog Box.
To Manage a bookmark – the created bookmarks can be removed by accessing View > Bookmark > Manage – to hold down the bookmarks and delete it.
To View the bookmark – the created bookmark will appear on View > Bookmark> (e.g. Whole Territory.)
Multiple Hyperlinks
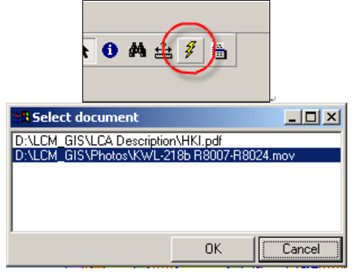
7.4.4 Hyperlinks provide additional ways to present more information on map features. The compatible type and format of documents can be a text file, image file (e.g. jpeg, bmp) or even web pages. It supports the creation of hyperlinks dynamically to let you browse the LCM.
7.4.5 Each LCA polygon is linked to it’s corresponding field survey photos. In addition, users can refer to a detailed description document of the LCA via the multiple hyperlink function. In the illustration below, field survey photos are stored in D:\LCM_GIS\Photos directory, while LCA description documents in PDF format are stored in D:\LCM_GIS\LCA Description folder. Users can click on a particular LCA polygon (e.g. HKI-315) on the LCM, using the Hyperlink tool, which will then open the dialog box, prompting the user to indicate the document he wants to open, as shown below. These documents can be either the survey photo or the LCA description report.
74.6 Field survey photos may have “.MOV” or “.JPG” or “.PDF” extensions. By choosing documents with “.MOV” or “.JPG” extensions, the following screen of LCA No. HKI-315 will be displayed:
7.4.7 If the user chooses a document with “.PDF” extension, the following screen will be displayed:
7.4.8 The corresponding summary report of LCA No. HKI-315 will be opened by the Acrobat Reader program. This is illustrated below.
7.4.9 Several steps are required for the creation of a hyperlink. These are as follows: